Risk Factors - Obesity in the Top 3
Obesity is one of the three greatest risk factors for suffering the most serious consequences of Covid-19, including age. The study give us insight into why Covid-19 has a more serious consequence for the obese and overweight. Fat cells express the receptor for SARS-CoV-2, serving as a reservoir for virus infection. Those who are overweight and obese remain infected several days longer than their aged-matched leaner counterparts. Moreover, obesity creates an underlying inflammatory condition, one that very likely exacerbates the inflammation caused by SARS-C0V-2 infection, one of the leading causes of Covid-19 disease.

Obesity increases risk of being Sicker and Dying
Not only does obesity increase your risk of being sicker and dying from COVID-19; obesity increases your risk of getting infected in the first place.
 onlinelibrary.wiley.com
onlinelibrary.wiley.com
You have a higher death rate risk at days 21 and 45 if you are obese
Higher rates of obesity in COVID-19 patients who are critically ill
 journals.lww.com
journals.lww.com
Obesity is associated with 236 medical diagnoses including 13 types of cancer

 obesitymedicine.org
obesitymedicine.org
In an analysis of data and studies from more than 160 countries, the researchers found that Covid-19 mortality rates increased along with countries' prevalence of obesity. They note that the link persisted even after adjusting for age and national wealth.
The report found that every country where less than 40% of the population was overweight had a low Covid-19 death rate of no more than 10 people per 100,000.
But in countries where more than 50% of the population was overweight, the Covid-19 death rate was much higher -- more than 100 per 100,000.

 edition.cnn.com
edition.cnn.com
Worse COVID-19 severity, higher risk of ICU, increased mortality (3.78 times more likely to die in hospitalisation)
Obesity
Risk of death and severity is about 3-4 times higher. Due to chronic inflammation in the system which then potentiates COVID-19 cytokine storm.
In patients with community-managed COVID-19 pneumonia, obesity is associated with a higher hospitalization risk and overall worse outcomes than for nonobese patients.

At a BMI of more than 23 kg/m2, we found a linear increase in risk of severe COVID-19 leading to admission to hospital and death, and a linear increase in admission to an ICU across the whole BMI range, which is not attributable to excess risks of related diseases. The relative risk due to increasing BMI is particularly notable people younger than 40 years and of Black ethnicity.

The findings from this study show an association between weight loss achieved with surgery and improved outcomes of COVID-19 infection, suggesting that obesity can be a modifiable risk factor for the severity of COVID-19 infection.

 www.contagionlive.com
www.contagionlive.com
Obesity is one of the three greatest risk factors for suffering the most serious consequences of Covid-19, including age. The study give us insight into why Covid-19 has a more serious consequence for the obese and overweight. Fat cells express the receptor for SARS-CoV-2, serving as a reservoir for virus infection. Those who are overweight and obese remain infected several days longer than their aged-matched leaner counterparts. Moreover, obesity creates an underlying inflammatory condition, one that very likely exacerbates the inflammation caused by SARS-C0V-2 infection, one of the leading causes of Covid-19 disease.

Association of Body Mass Index and Other Metabolic Risk Factors with Pneumonia Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients with Coronavirus Disease-19: An International Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study
Previous studies unveiled a relation between COVID-19 severity and obesity. The aims of this multicenter retrospective cohort study were to disentangle the asso
papers.ssrn.com
Obesity increases risk of being Sicker and Dying
Not only does obesity increase your risk of being sicker and dying from COVID-19; obesity increases your risk of getting infected in the first place.
Error - Cookies Turned Off
 onlinelibrary.wiley.com
onlinelibrary.wiley.com You have a higher death rate risk at days 21 and 45 if you are obese
Higher rates of obesity in COVID-19 patients who are critically ill

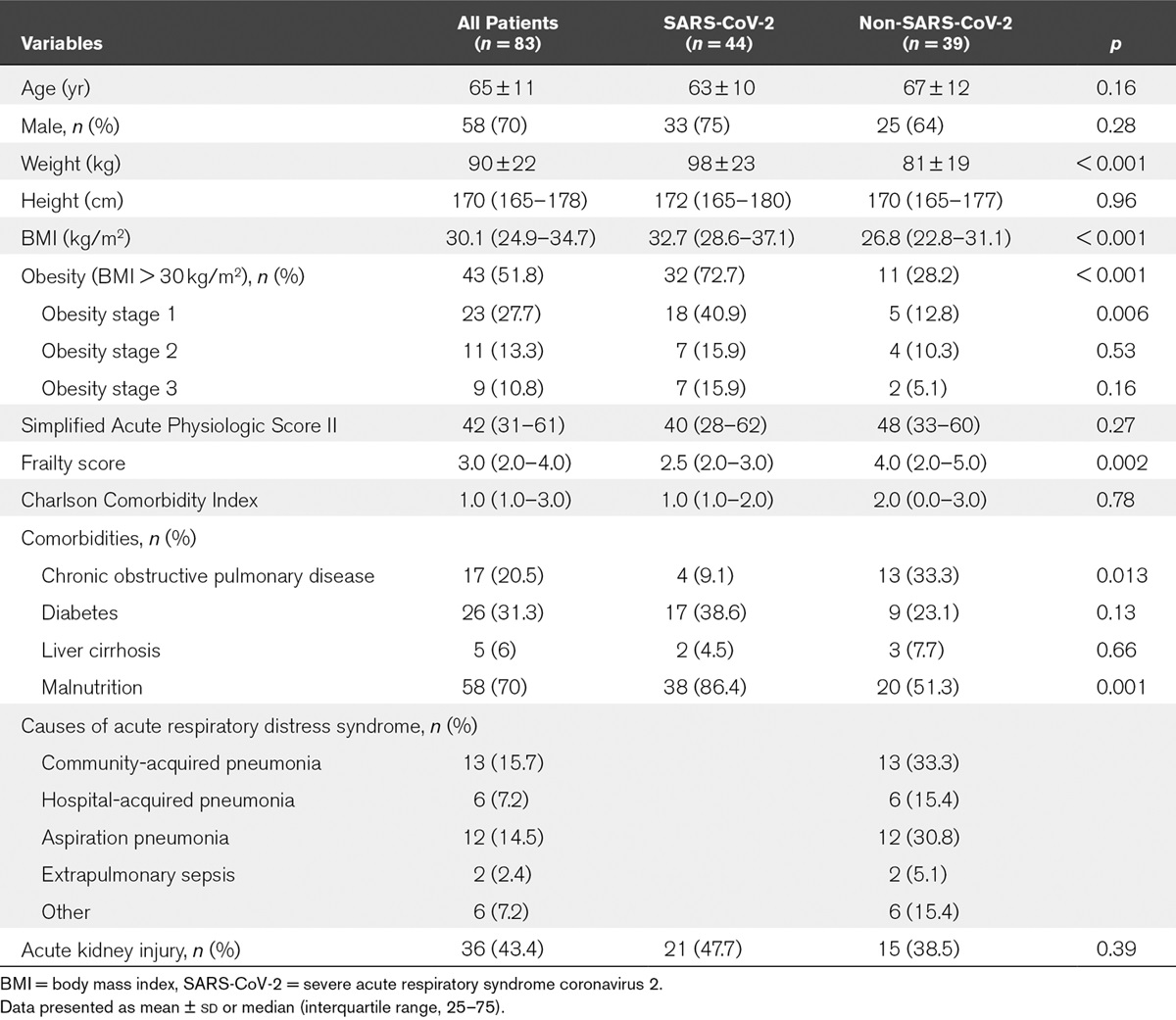
Implications of Obesity for the Management of Severe... : Critical Care Medicine
tudy. Setting: A 34-bed ICU of a tertiary hospital. Patients: The first 44 coronavirus disease 2019 acute respiratory distress syndrome patients were compared with a historical control group of 39 consecutive acute respiratory distress syndrome patients admitted to the ICU just before the...
Obesity is associated with 236 medical diagnoses including 13 types of cancer

What Is Obesity?
Obesity is defined by the World Health Organization (WHO) as “abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that presents a risk to health.” The disease of obesity affects more than one-third of U.S.
In an analysis of data and studies from more than 160 countries, the researchers found that Covid-19 mortality rates increased along with countries' prevalence of obesity. They note that the link persisted even after adjusting for age and national wealth.
The report found that every country where less than 40% of the population was overweight had a low Covid-19 death rate of no more than 10 people per 100,000.
But in countries where more than 50% of the population was overweight, the Covid-19 death rate was much higher -- more than 100 per 100,000.

Covid-19 death rates 10 times higher in countries where most adults are overweight, report finds | CNN
The risk of death from Covid-19 is about 10 times higher in countries where more than half of the population is overweight, according to a report released Wednesday by the World Obesity Forum.
Worse COVID-19 severity, higher risk of ICU, increased mortality (3.78 times more likely to die in hospitalisation)

Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, and COVID-19: A Review of Evidence
In this OE Original, we examine current evidence with regard to the impacts of obesity or diabetes mellitus on patients with COVID-19. We also discuss COVID-19 vaccination in these vulnerable populations.
myorthoevidence.com
Obesity
Risk of death and severity is about 3-4 times higher. Due to chronic inflammation in the system which then potentiates COVID-19 cytokine storm.
In patients with community-managed COVID-19 pneumonia, obesity is associated with a higher hospitalization risk and overall worse outcomes than for nonobese patients.

Obesity is a Major Risk Factor for Hospitalization in Community-Managed COVID-19 Pneumonia
We aimed to investigate whether the stratification of outpatients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia by body mass index (BMI) can help predict hospitalization and other severe outcomes.
www.mayoclinicproceedings.org
At a BMI of more than 23 kg/m2, we found a linear increase in risk of severe COVID-19 leading to admission to hospital and death, and a linear increase in admission to an ICU across the whole BMI range, which is not attributable to excess risks of related diseases. The relative risk due to increasing BMI is particularly notable people younger than 40 years and of Black ethnicity.

Associations between body-mass index and COVID-19 severity in 6·9 million people in England: a prospective, community-based, cohort study
At a BMI of more than 23 kg/m2, we found a linear increase in risk of severe COVID-19 leading to admission to hospital and death, and a linear increase in admission to an ICU across the whole BMI range, which is not attributable to excess risks of related diseases. The relative risk due to...
www.thelancet.com
The findings from this study show an association between weight loss achieved with surgery and improved outcomes of COVID-19 infection, suggesting that obesity can be a modifiable risk factor for the severity of COVID-19 infection.

Successful Weight-Loss Surgery Reduces Risk of Severe COVID-19
COVID-19 patients who underwent prior weight-loss surgery were significantly less likely to experience severe disease outcomes.
Last edited: